1.1 Sensor:
A device which senses the physical changes in the surrounding and converts into a reliable quantity or electrical signal.
Classification of Sensor (Based on Physical Parameter)
1.Temperature
2.Pressure
3.Flow
4.Level
5.Proximity
6.Bio parameter
7.Gas and chemical
8.Humidity ,speed.
Classification of Sensor (Based on application)
1.Industrial Process control
2.Medical Application
3.Aircraft control
Classification based on technology used:
1.Thermal sensor
2.Optical sensor
3.Magnetic sensor
4.Electric sensor
1.2 Thermal sensor
Application :used for temp. measurement
Types of Thermal Sensor
A) Contact type
1) Thermocouple
2) RTD
3) Thermistor
4) IC/Semiconductor type (example LM35)
•Voltage output
•Digital output
•Analog Output
•Resistance Output
5) liquid in glass
B)Non contact type
Pyrometer
Liquid in Glass Thermal sensor
Figure 1. Liquid in glass Thermal Sensor.
Working Principle:-
The liquid-in-glass (LiG) thermometer is one of the most common thermometers used now a day. A LiG thermometer, by definition,consist a liquid-filled bulb at bottom and a glass capillary tube at another side as temperature of liquid increases, it expands and rises into capillary tube.
The level marked on the outer side of the liquid in the column corresponds to a specific temperature.
Usually liquid used in thermometer is mercury, toluene and low-hazard biodegradable liquids.
Advantages:
cheap cost
simple to use
do not require external power for functioning
reasonably accurate
Disadvantages:
Delicate
Not highly accurate
Human error are more.
Non contact type: Pyrometer
Optical sensor family.
Used in metallurgy to measure temp of hot molten metal.
The object at high temp radiates infrared energy at wavelength of above 0.78 micron.
This energy is captures and passed onto optical sensor.
Types of pyrometer
A) Radiation Pyrometer
B) Optical Pyrometer
C) Photoelectric Pyrometer
A) Radiation Pyrometer:
Figure 2 : Radiating Pyrometer.
Temperature range 1200 -3500 degree Celsius.
Does not make direct contact with hot body but pick up radiation of hot body with a tube
aperture arrangement.
The radiation are applied on thermocouple or thermopile.
The law of radiation is given by the expression:
W= K(T4 -T04) ( 2.1)
W- energy per square meter per second received by cold body
K- constant (value is obtained through experimentation)
T- Absolute temperature of hot body
T0 -Absolute temperature of surrounding
Radiation Pyrometer are of Two types :
Fixed Focus Type
Variable Focus Type
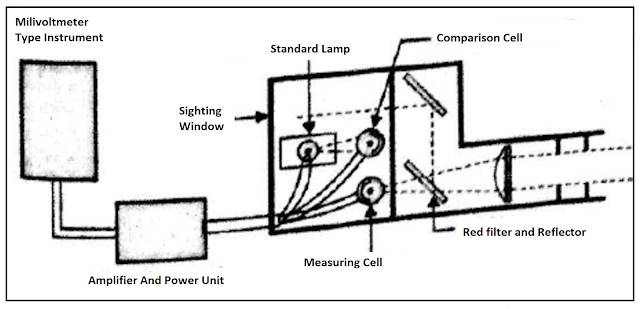
Optical Pyrometer:
Photoelectric Pyrometer:
Figure 03.Photoelectric Pyrometer
Operates on the principle of automatically matching the radiation from standard source and
radiation from target surface.
Lens concentrate the radiation from hot body to sighting tube,the photo emissive vacuum
tube produces an electron current which is proportional to radiation intensity.
the response from photo tube is amplified with an amplifier unit.
Optical Sensor
Light Signal -> Electrical Signal
Optical sensor Classification Based On Output signal :
•Photoconductive- Change in light causes change in resistance can change in
electrical output
•Photovoltaic- change in incident light causes change in output voltage.
•Photodiode- change in incident light causes change in output voltage.
Optical sensor Classification Based On transmitter receiver used :
•Through beam sensor
•Retro reflective sensor (reflected from rotor/shaft)
•Diffuse reflection sensor (Led, Laser)
Advantages of optical sensor
•Operation not affected by external magnetic field
•Remote operation
•Can be used in hazardous or explosive environment
•Compact size
•Convenient arrangement
Disadvantage:
malfunction due to interference of light
Magnetic Sensor
Magnetic Field à Electric signal
Types of Magnetic Sensor
•Low range magnetic field sensor
•Earth magnetic field sensor / medium range
•BIAS Magnetic field sensor
•
Low range magnetic field sensor
1) Super conducting Quantum interface Device (SQUID)
•Josephson effect
•Current is passed through super conducting loop
•When a magnetic field is not present around the loop current is distributed uniformly.
Figure 04: Josephson Junction.
Application:
•Used in biology field
•MEG (Magnetoencephalography) which maps the neural activity inside brain.
•Cardiology
2) Fiber Optic sensor –Polarization Processing—detect magnetic field
Earth magnetic field sensor / medium range
Uses Earth magnetic field for navigation and vehicle detection
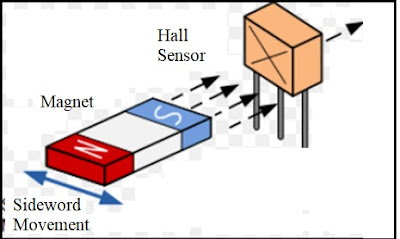
Example: 1. Hall effect sensor 2. Magneto resistor
Figure:05 Hall Sensor.
Figure 06:Hall Effect.
When semiconductor material carrying current kept perpendicular to magnetic field it produces emf at edges.




The Forehead and Surface Infrared Thermometer from SantaMedical is specially designed to obtain the most accurate temperature readings of tear ducts or the forehead. The temperature on the forehead reads from 1” to 4” away.
ReplyDeleteLiquid Level Sensor can be used to identify the level of substances that can flow. There are various types of liquid level sensor used to detect the point level of a liquid. Some types use a magnetic float, which rise and fall with the liquid in the container.
ReplyDeleteLiquid Level Sensor